APIs
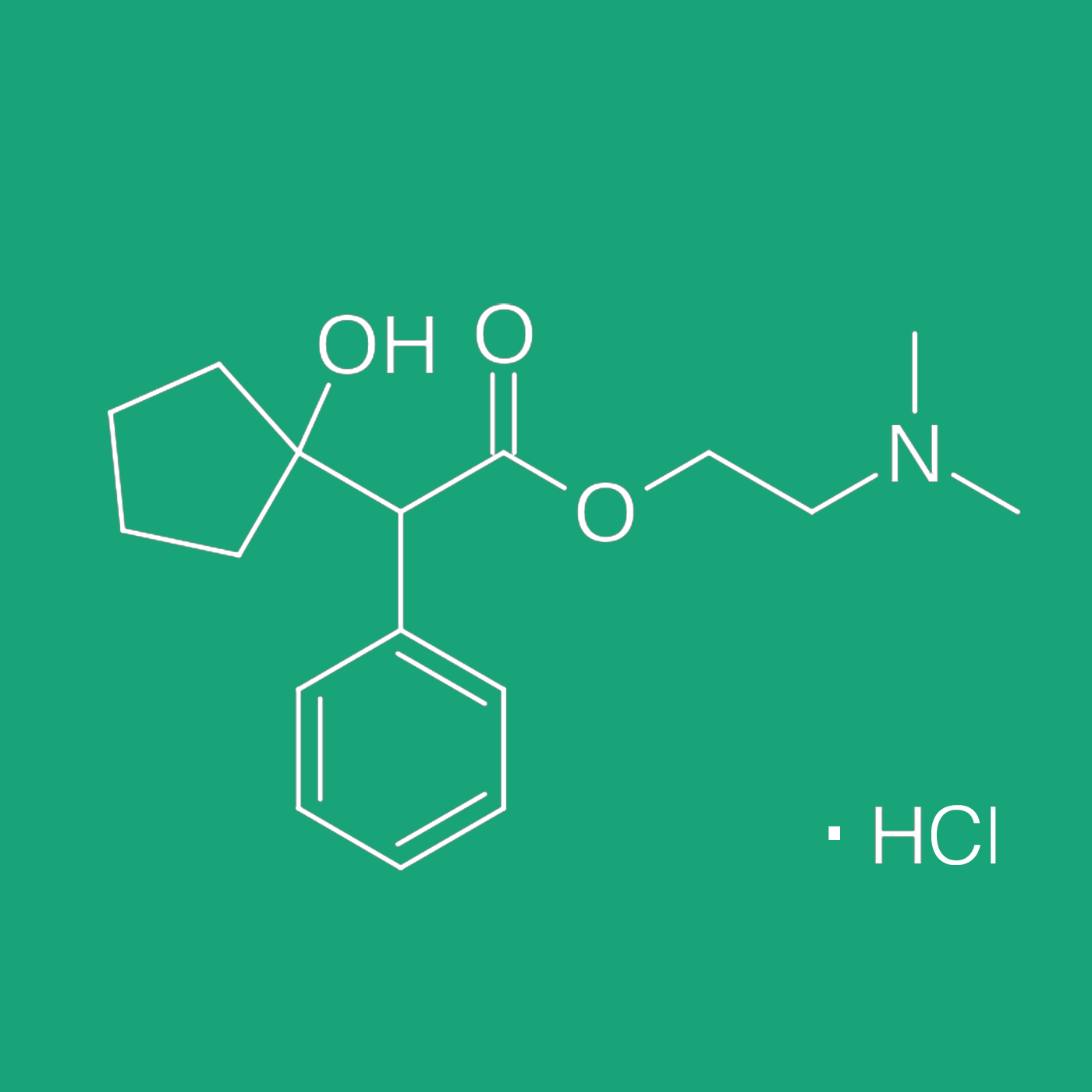
CYCLOPENTOLATE HYDROCHLORIDE
Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride is a synthetic muscarinic receptors antagonist that was first developed in the ‘50s by Schieffelin1,2 as a chemical analogue of atropine. It is a widely accepted drug of first choice for patients of all ages which provides excellent short-term cycloplegia and is therefore on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.3
USES
As a 0.5%, 1% or 2% topical ophthalmic solution Cyclopentolate is used for cycloplegic refraction and diagnostic pupil dilation. Cyclopentolate can also be administered to reverse muscarinic and central nervous system effects of indirect cholinomimetic (anti-AChase) administration.4
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Cyclopentolate blocks the action of acetylcholine to produce relaxation of the sphincter muscle of the iris resulting in dilation of the pupil (mydriasis). This agent has an anticholinergic effect similar to atropine. Paralysis of accommodation (cycloplegia) is produced by blocking cholinergic stimulation of the ciliary muscle of the lens.4
REFERENCES
- Patent US000002554511A, 1951.
- Treves, G. R., Testa, F. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74(1), 46–48.
- World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533.
- Clinical Ocular Pharmacology, 5th Edition, Bartlett, 2008. Chapter 9: Cycloplegics.